Earlier this spring, while much of the nation’s attention focused on the coronavirus crisis, the U.S. oil and gas industry quietly launched a new coalition using messaging that invokes “transportation fairness.” Like other petroleum interest front groups that have campaigned against clean transportation measures, this new coalition appears poised to counter policies designed to accelerate the transition away from petroleum-powered transportation.
The Transportation Fairness Alliance (TFA), as the new coalition is called, describes itself as “a diverse partnership of businesses, associations, and organizations that support a competitive and equitable transportation sector. Collectively, we represent our nation’s manufacturers, small business owners, farmers, and folks who pay utility bills.”
Despite claims of “diversity” and “equity,” the coalition is comprised mainly of oil and gas trade associations with a vested interest in maintaining the petroleum-dependent transportation system status quo. Logos for these trade associations appear near the bottom of the website’s “About Us” section, making it no secret who is funding and driving this new alliance.
The American Petroleum Institute, the powerful U.S. oil and gas lobbying group, led the creation of the Transportation Fairness Alliance, DeSmog has learned. The American Fuel and Petrochemical Manufacturers, Independent Petroleum Association of America (IPAA), Petroleum Marketers Association of America, and the American Public Gas Association are all involved as well. The American Farm Bureau Federation, Agricultural Retailers Association, and a trucking group called the National Tank Truck Carriers are also involved.
The bottom line is that these organizations represent the business interests of the petroleum and agriculture (i.e., biofuel) industries, which stand to lose profits from the electrification of the transportation system and increases in fuel efficiency. Public relations firm FTI Consulting, which manages other fossil fuel advocacy websites such as IPAA’s Energy in Depth, is also behind the Transportation Fairness Alliance website and the coalition’s communications.
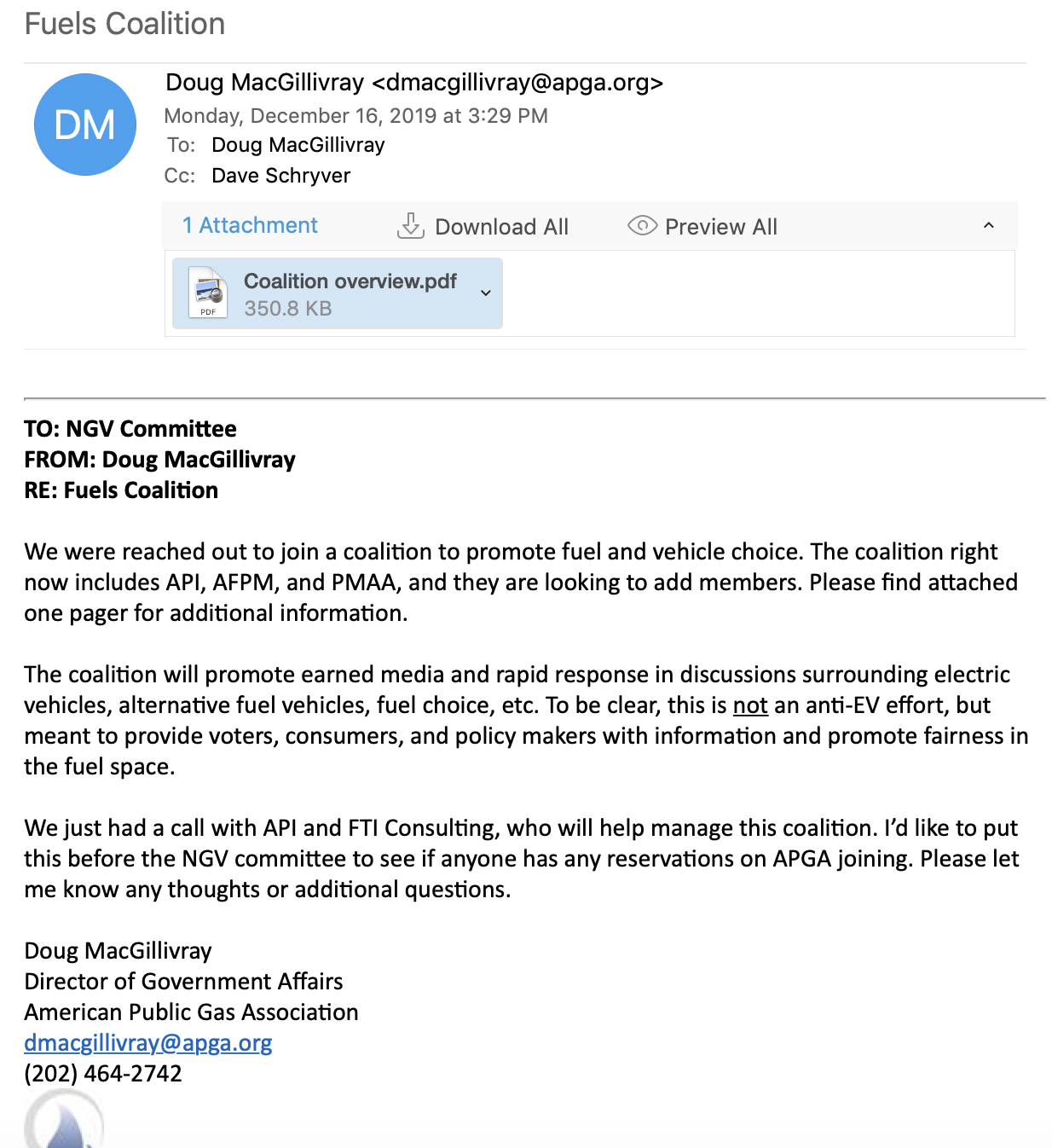
Email from American Public Gas Association’s Doug MacGillivray with details about the Transportation Fairness Coalition’s mission and partners.
According to an email obtained by DeSmog, the coalition “will promote earned media and rapid response in discussions surrounding electric vehicles, alternative fuel vehicles, fuel choice, etc.” While Doug MacGillivray of the American Public Gas Association says in the December 2019 email that “this is not an anti-EV effort,” the coalition’s stated positions oppose policies that would speed the transition towards an electrified transportation system, often relying on misleading and deceptive claims.
According to Keiko Budech, communications manager for the Transportation Choices Coalition, a nonprofit advocating for accessible transportation in Washington state, a truly “fair and equitable” transportation system would focus on the needs of disadvantaged communities such as communities of color, people with disabilities, and families with low income.
“That means focusing on building a transportation system that reduces climate pollution, improves community health, and increases access to opportunity by investing more in transit service, multimodal programs, and safer transportation infrastructure that prioritizes people over cars,” said Budech.
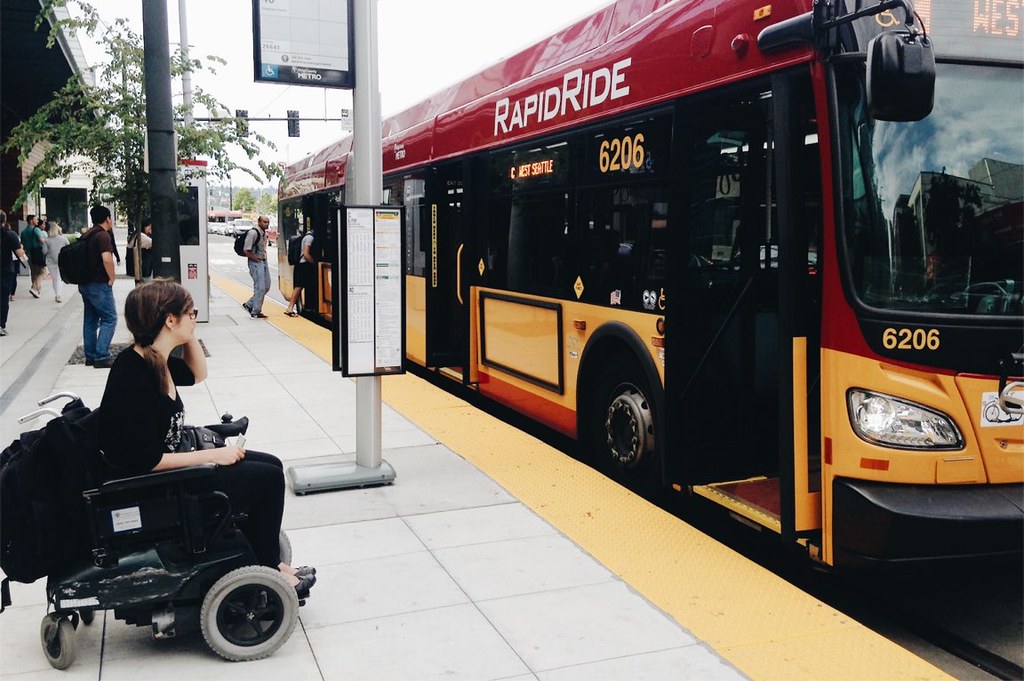
A rider in a wheelchair waits to board a RapidRide bus in Seattle, Washington. Credit: SDOT, CC–BY–NC 2.0
Neither API nor FTI Consulting responded to requests for comment.
Debunking TFA’s Position Statements
The coalition outlines its policy positions and statements of principle on its website. Many rely on easily debunked talking points and cherry-picked data that have been perpetuated by the oil industry for years.
For example, TFA writes on its website:
Everyone who uses our roads should help pay for their construction and upkeep.
Some states already charge annual fees for electric vehicles (EV). Collecting these types of usage or registration fees is seen as a way to make up for lost revenue because EV drivers do not pay any gas taxes, which help fund things like road maintenance. Congressional Republicans have also introduced federal legislation that would end the EV tax credit and require EV drivers to pay a fee, which would go into the Highway Trust Fund. That policy proposal also uses the “fairness” messaging, as the legislation is titled the “Fairness for Every Driver Act.”
But, as the Sierra Club has pointed out, EV fees actually do little to close state revenue gaps, and EV owners contribute more to other revenue streams like the excise tax and state sales tax than drivers of gas-powered cars. According to a 2019 Consumer Reports analysis, proposed fees on electric vehicles will only contribute an average of 0.04 percent of current state highway funding. That analysis also found that (as of 2016) the gas tax accounted for less than 29 percent of state revenues directed towards highway funding, meaning that roads are funded by a lot of other sources that EV drivers do contribute to.
Furthermore, the gasoline that fuels conventional cars contributes to air pollution and carbon emissions. However, at the moment, there is no cost or penalty imposed on tailpipe emissions. “It is rather disingenuous to claim seeking ‘fairness’ for the costs of road usage but then not to seek fairness for the costs of unhealthy air that harms everyone,” Sierra Club explains.
Another TFA statement asserts that:
Utilities should not raise rates for everyone to cover the cost of EV infrastructure and chargers that serve only a very few.
While EVs are still a minority in the road transport sector, they are increasing in drivership and becoming more affordable for middle and lower-income consumers.
Electric vehicle infrastructure is also expanding and utilities are — and many argue should be — investing in it. And utility investment doesn’t necessarily cause higher electricity rates.
According to an analysis published in June 2019 by Synapse Energy Economics, “If done carefully, utility-funded investments can deliver benefits to all ratepayers in excess of their costs.” That analysis found that “increased EV adoption in the two utility service territories with the most EVs in the United States has already resulted in more electricity revenues than costs,” concluding “EV adoption can reduce costs for both EV-drivers and other electric customers while reducing harmful emissions.”
TFA also advocates that:
Government transportation incentives should not be directed toward competitive technologies that have reached commercial scale.
Without saying it directly, this statement implies that the electric vehicle tax credit — a favorite target of EV opponents — should be discontinued. According to this statement, electric vehicles don’t need a tax credit because they are a “competitive technology,” but this is misleading. Electric vehicles are still a relatively newer technology, especially compared to gas-powered vehicles.
As the International Energy Agency (IEA) explained in a recent commentary, “Electric cars are gradually becoming competitive in some countries on the basis of the total cost of ownership … But the high upfront investment for consumers — electric car prices are still higher than those of conventional cars — mean that the electric car market still relies on government support.” Incentives like the EV tax credit help lower the upfront cost or can help reduce the base cost of a lease, making EVs more affordable.
Furthermore, while EV opponents argue that electric cars shouldn’t get government incentives, they ignore the many subsidies and incentives that go to fossil fuels. These subsidies total much more than the EV tax credit.
Fighting Transportation Electrification
The Transportation Fairness Alliance appears to be the latest public relations front coordinated by oil and gas interests to fight the electrification of the transportation system, which is now the largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. According to the IEA, electric vehicle sales “could reach a record share of the overall [global] car market this year.” For companies that produce and refine gasoline (and ethanol), this trend is undoubtedly concerning.
Even disregarding the environmental advantages of eliminating tailpipe emissions, electric vehicles have an inherent economic advantage — eliminating consumer spending on gasoline — that will likely ensure the electrification trend continues.
“People are fed up with instability,” said Max Baumhefner, senior attorney at the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) who focuses on clean energy and electric transportation. “Gas prices are down now, but we all know they will shoot up. We just don’t know when. In contrast, driving on electricity is the cost equivalent of driving on dollar-a-gallon gasoline and it’s been that way for the last 30 years.”
“All the growth in transportation is being eaten by electricity,” Harry Benham, chairman of Ember-Climate, a British energy transition think tank, recently told Reuters. “Oil and gas companies have got no ability to defeat electricity as a transport fuel.”
But as the emergence of the Transportation Fairness Alliance indicates, they surely are going to try.
Main image: “yellow ~ 9 gas pump tabs” Credit: Upupa4me, CC BY–SA 2.0
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts